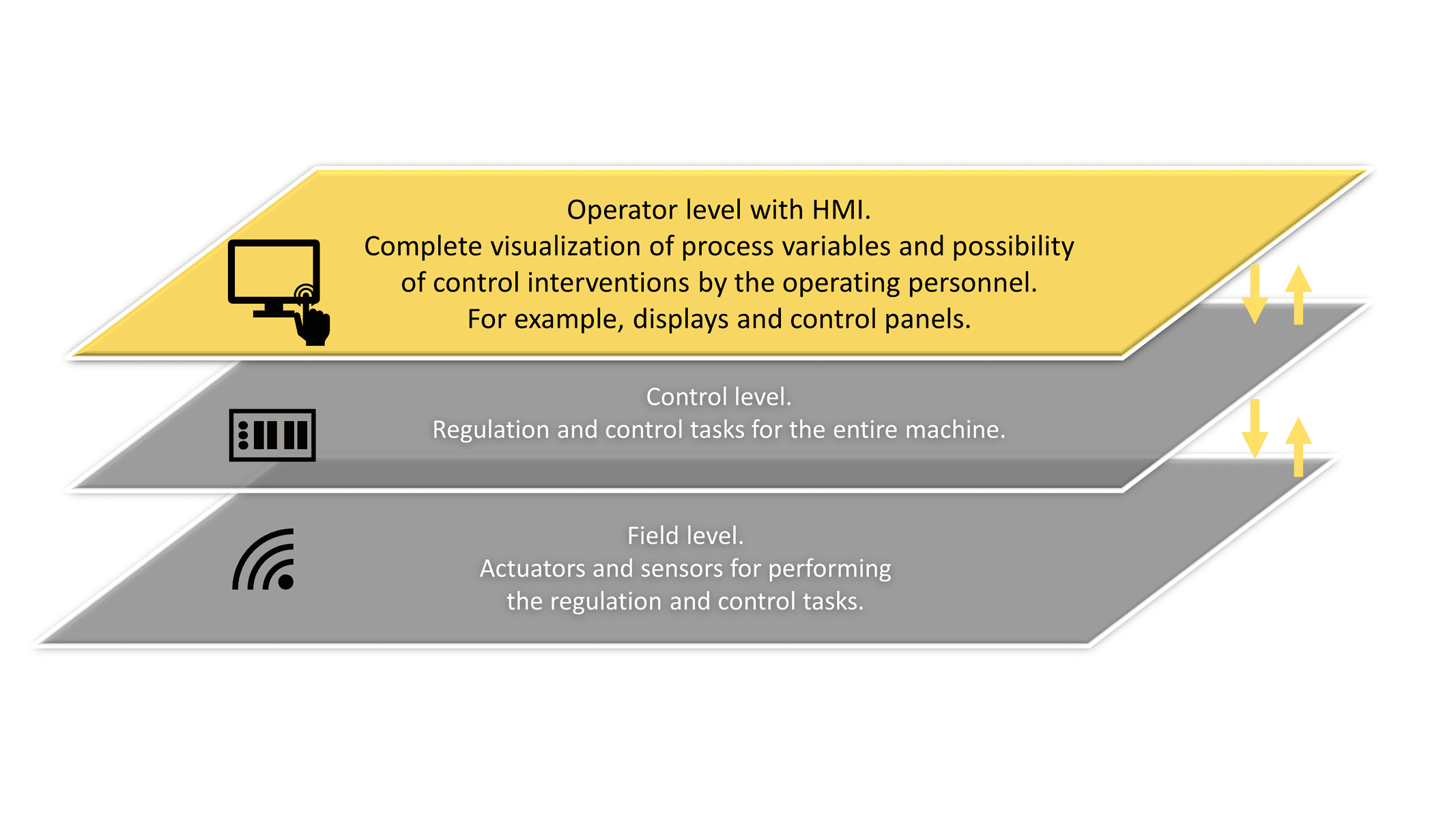
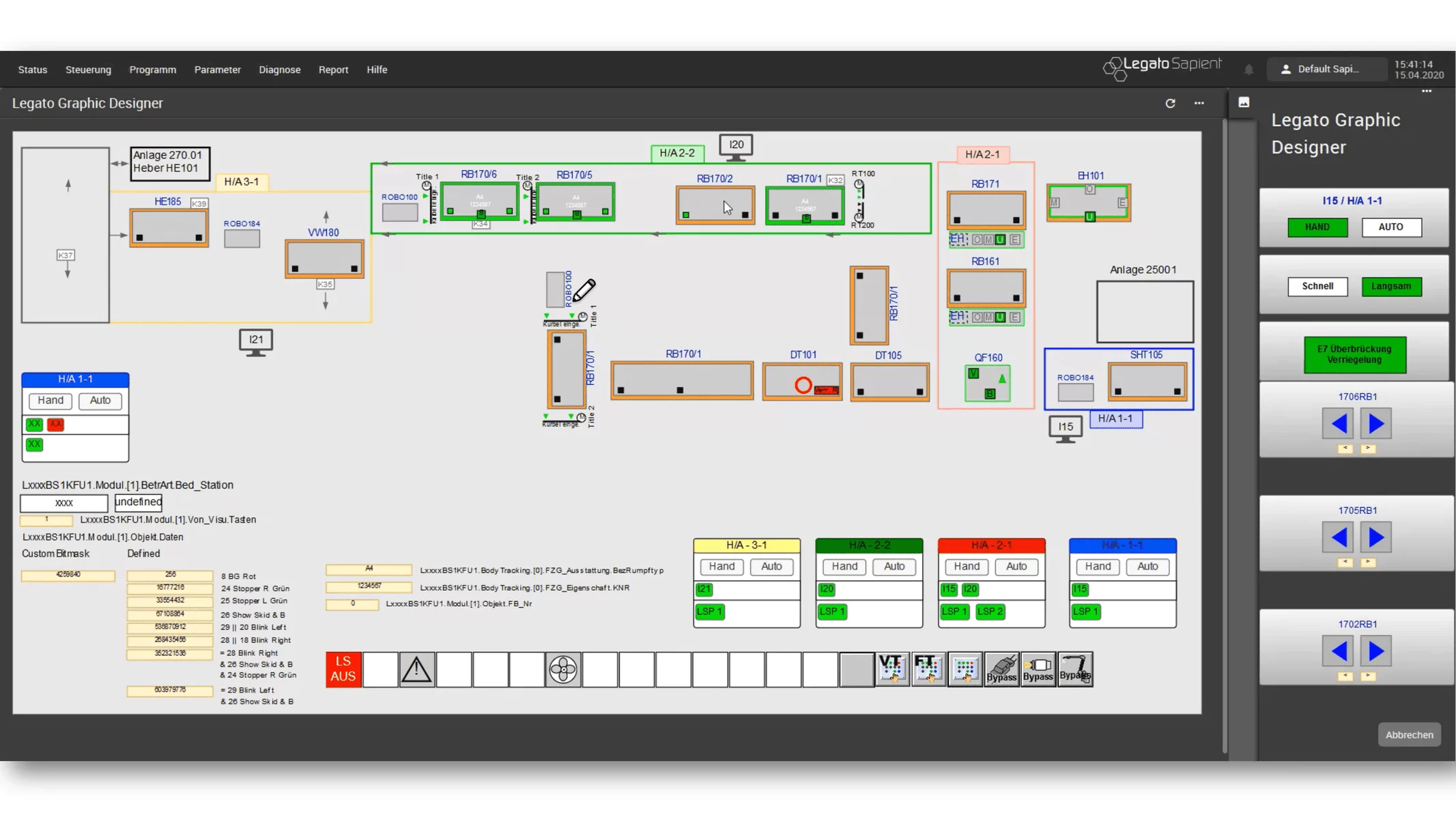
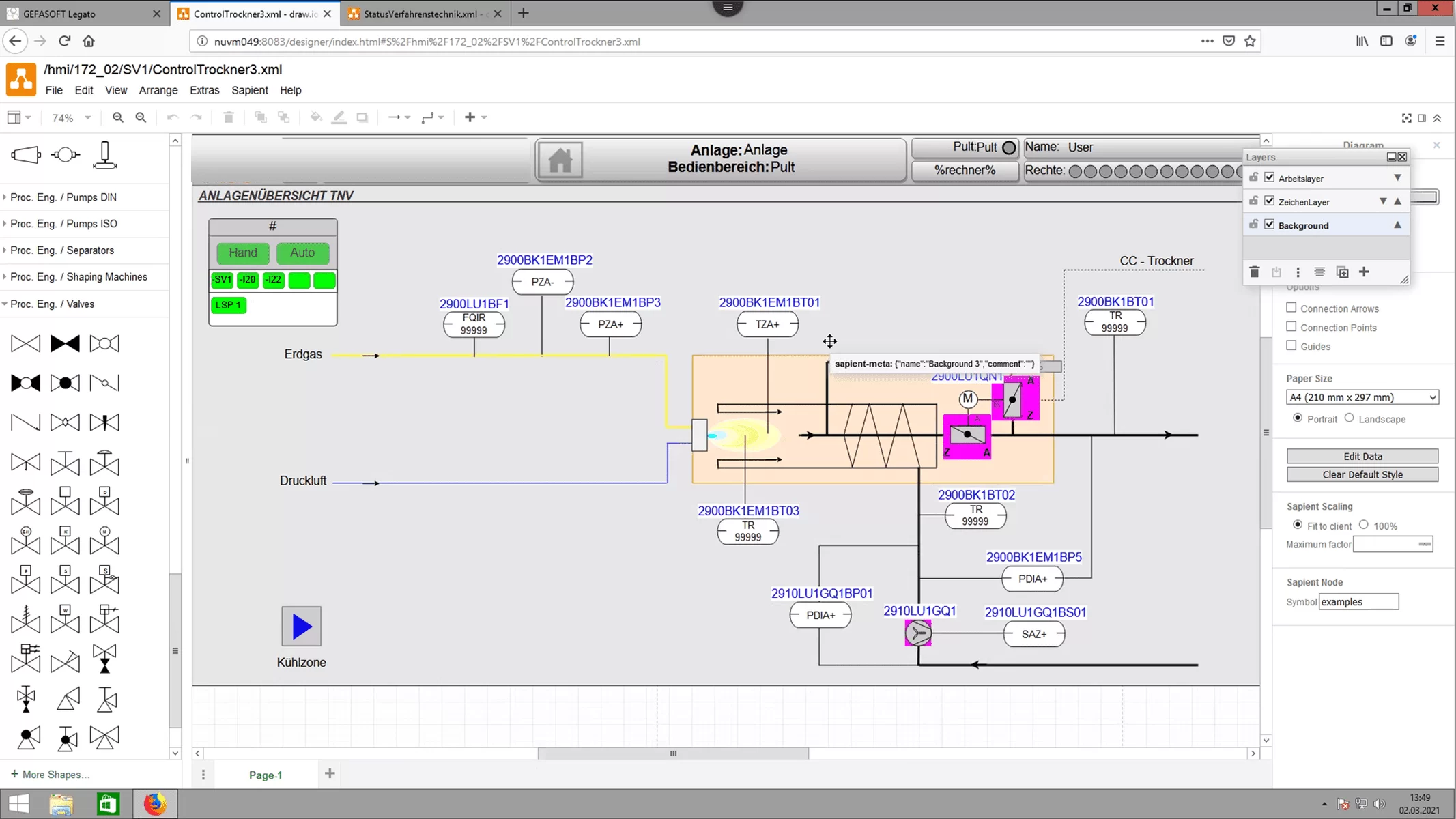
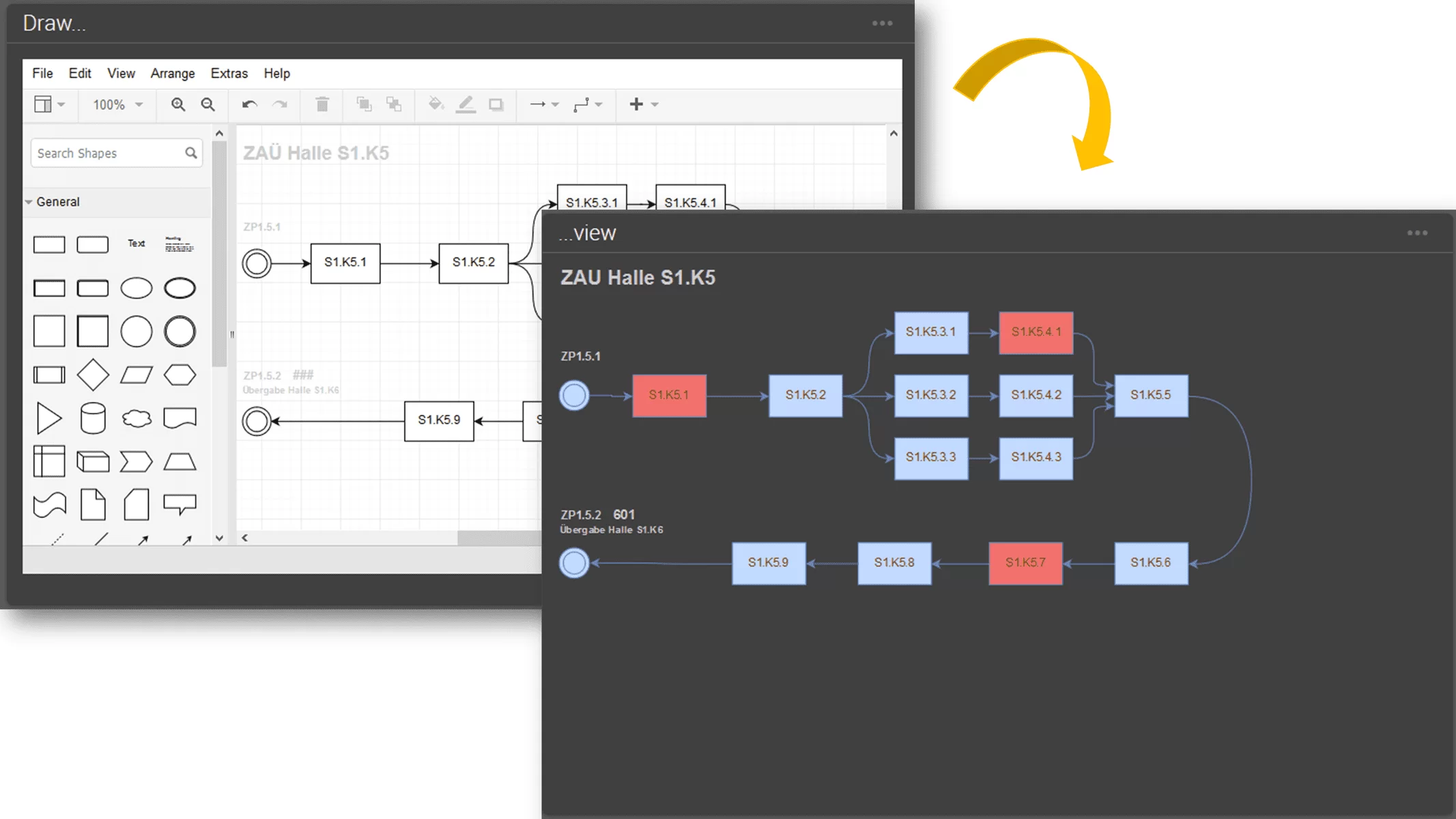
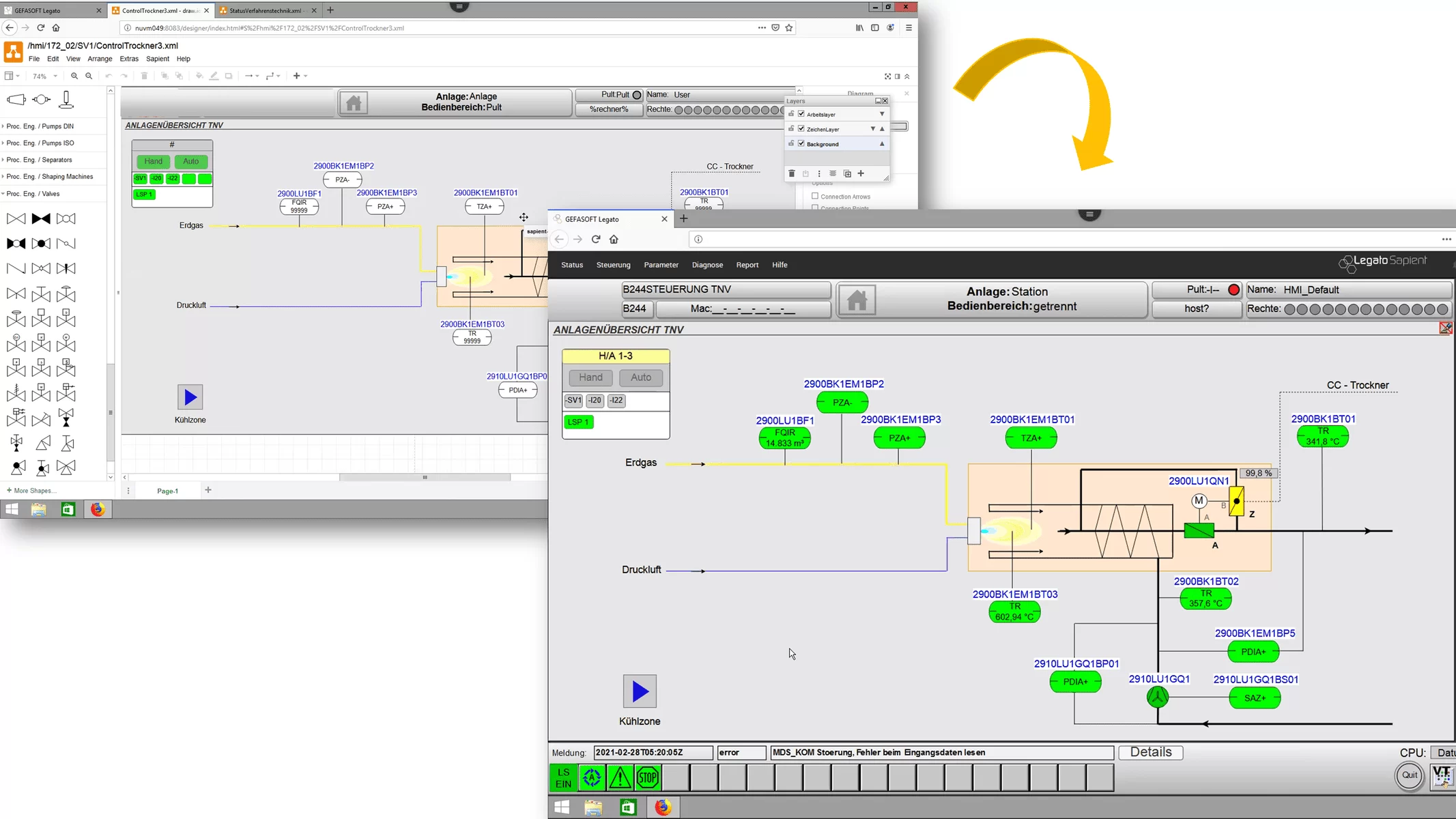
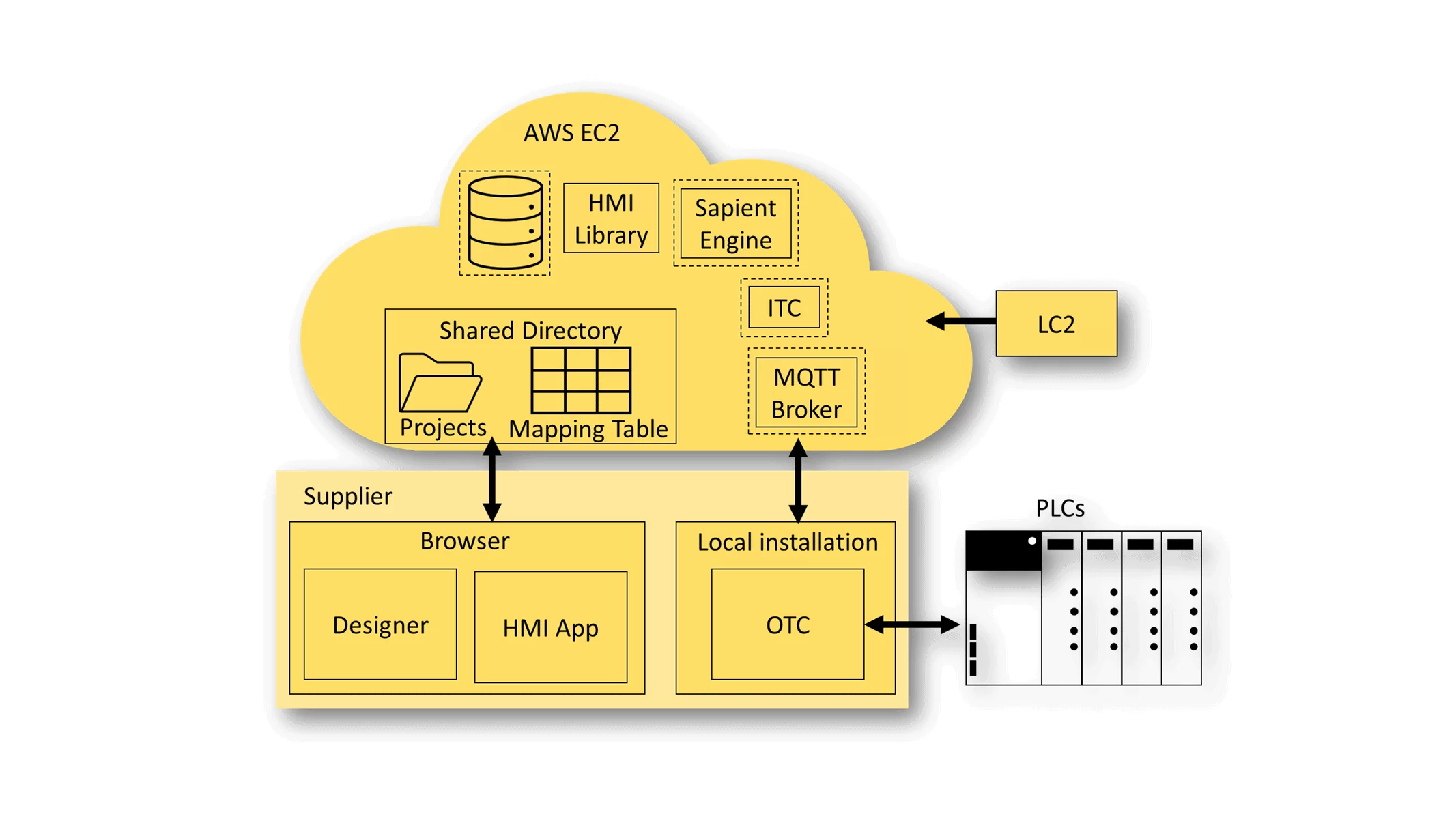
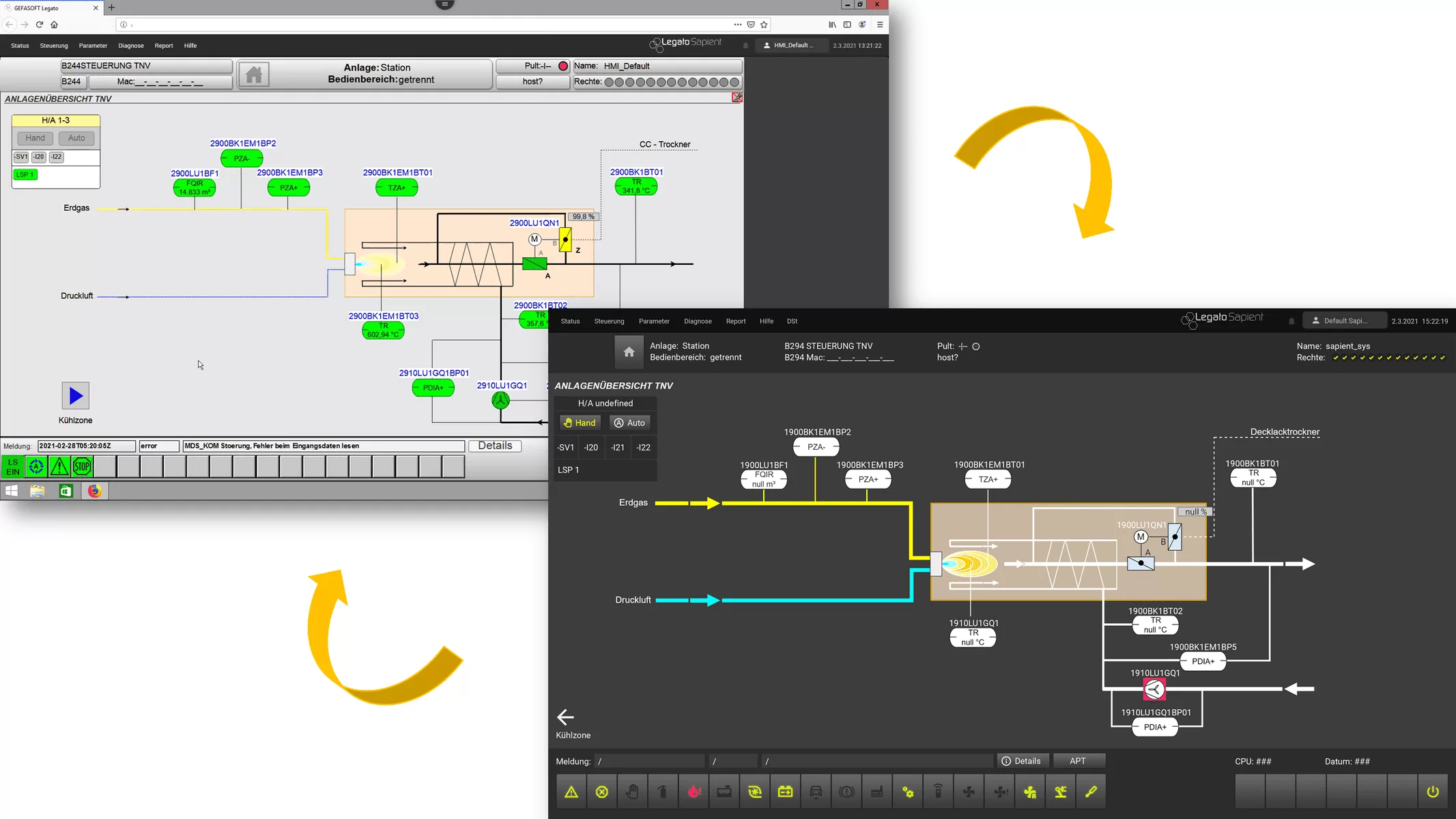
Due to the increasing complexity of the machines, it is becoming more and more important to be able to display a large amount of information in a small space. At the same time, however, this information must also be displayed in a way that makes sense to the worker according to ergonomic points, so that he can grasp and react to it quickly.
An HMI (Human Machine Interface) deals with two areas, on the one hand the clear display of information and on the other hand the simple operation of the machine.